Positive Health Online
Your Country

A Healthy Liver and Weight Loss
listed in detoxification, originally published in issue 37 - February 1999
The liver has everything to do with how we live – that's why it is called the "liver". The state of your liver will have a huge bearing upon how well you live, how long you will live and how you will look and feel.
In today's world the liver has to work harder than ever and all over the world we find that liver problems are increasing. Globally one in every ten people suffers with some type of liver disease. This is increasing and thousands of people are waiting anxiously for liver transplants that many of them will never be lucky enough to receive. There are just not enough donor livers to keep up with the demand.
Even more commonly people suffer with a dysfunctional liver, which means that the liver is not working efficiently and is overloaded, toxic and sluggish. In my experience over 25 years of clinical medicine I have found that approximately one in every three persons has a dysfunctional liver.
|
What are the symptoms of a dysfunctional liver? |
|
|
Abnormal metabolism of fats (lipids) leading to – External signs Digestive Problems |
Nervous System Immune dysfunction Blood Sugar Problems Hormonal imbalance |
Symptoms of Liver Dysfunction
Many people suffer with symptoms and signs of a dysfunctional liver for years and yet the treating doctor or naturopath does not recognise the significance of these symptoms. The result is that the symptoms get treated while the underlying problem of an overloaded, toxic and inefficient liver is ignored or only partially treated.
Inevitably the patient's symptoms deteriorate and increasing doses of drugs such as antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, immuno-suppressants, pain killers, cholesterol lowering drugs, etc. are needed. The full range of symptoms indicative of "dysfunctional liver syndrome" can only be defined after a study of Eastern and Western medical disciplines. Chinese doctors have long considered the liver to be the most important organ in the body and indeed they call the liver, "the general of the army" of the body. I consider the liver to be the most strategic organ in the body because by improving its function we are able to help many other body systems.
The Liver And Detoxification
More than ever before in the history of mankind human beings need to have healthy livers to break down the chemicals that have crept into our environment.
The liver is the gateway to the body and in this chemical age its detoxification systems are easily overloaded. Thousands of chemicals are added to food and over 700 have been identified in drinking water. Plants are sprayed with toxic chemicals, animals are injected with potent hormones and antibiotics and a significant amount of our food is genetically engineered, processed, refined, frozen and cooked. All this can lead to destruction of delicate vitamins and minerals, which are needed for the detoxification pathways in the liver. The liver must try to cope with every toxic chemical in our environment, as well as damaged fats that are present in processed and fried foods.
The Liver Filter
If we examine the liver under a microscope we will see rows of liver cells separated by spaces which act like a filter or sieve through which the blood stream flows. The liver filter removes toxic matter (such as dead cells, micro-organisms, sludge and chemicals) from the blood stream. The liver filter is called the sinusoidal system and contains specialised cells known as Kuppfer cells which ingest and breakdown the above mentioned toxic matter.
The liver is the cleanser and filter of the blood stream and is of vital importance.

The Liver Detoxification Pathways
Inside the liver cells there are sophisticated mechanisms that have evolved over millions of years to break down toxic substances. Every drug, artificial chemical, pesticide and hormone is broken down (metabolised) by enzyme pathways inside the liver cells.
Many of the toxic chemicals that enter the body are fat-soluble which means they dissolve only in fatty or oily solutions and not in water. Fat-soluble chemicals have a high affinity for fat tissues and cell membranes, which are made of fatty substances. In these fatty parts of the body toxins may be stored for years, being released during times of exercise, stress or fasting. During the release of these toxins, symptoms such as headaches, poor memory, stomach pain, nausea, fatigue, dizziness and palpitations may occur.
The liver is designed to convert fat-soluble chemicals into water-soluble chemicals so that they may then be easily excreted from the body via watery fluids such as the bile and urine.
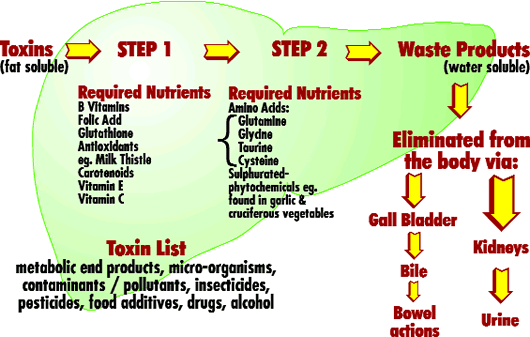
Detoxification Pathways
How The Liver Detoxifies Harmful Substances
Basically there are two major detoxification pathways inside the liver cells which are called the Phase One and Phase Two detoxification pathways.
Phase One Detoxification Pathway
An example of the Phase One pathway is the Cytochrome P-450 system. This converts a toxic chemical into a less harmful chemical. This is achieved by various chemical reactions (such as oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis, hydroxylation) and during this process free radicals are produced which if excessive, can damage the liver cells. Antioxidants (such as vitamin C and E and natural carotenoids) reduce the damage caused by these free radicals. If antioxidants are lacking, toxic chemicals become far more dangerous.
Excessive amounts of toxic chemicals such as pesticides can disrupt the P-450 system.
Phase Two Detoxification Pathway
This is called the conjugation pathway whereby the liver cells add another substance (e.g. glycine or a sulphur molecule) to a toxic chemical or drug to render it less harmful. This makes the toxin or drug water-soluble so it can then be excreted from the body via watery fluids such as bile or urine. Through conjugation the liver is able to turn drugs, hormones and various toxins into excretable substances. For efficient phase two detoxification the liver cells require sulphur containing amino acids such as taurine and cysteine. The nutrients, glycine, glutamine, choline and inositol are also required for efficient phase two detoxification. Eggs and cruciferous vegetables (e.g. broccoli, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower) and raw garlic, onions, leeks and shallots are all good sources of natural sulphur compounds to enhance phase two detoxification. Thus these foods can be considered to have a cleansing action.
The phase two enzyme systems include both UDP-glucuronyl transferase (GT) and glutathione-S-transferase (GSH-T). Glutathione is the most powerful internal antioxidant and liver protector. It can be depleted by large amounts of toxins and/or drugs passing through the liver as well as starvation or fasting.
Toxic Overload
If the Phase One and Two detoxification pathways become overloaded there will be a build up of toxins in the body. Many of these toxins are fat-soluble and incorporate themselves into fatty parts of the body where they may stay for years, if not for a lifetime. The brain and the endocrine (hormonal) glands are fatty organs, and are common sites for fat soluble toxins to accumulate. This may result in symptoms of brain dysfunction and hormonal imbalances such as infertility, breast pain, menstrual disturbances, adrenal gland exhaustion and early menopause. Many of these chemicals (e.g. pesticides, petrochemicals, aspartame etc.) are carcinogenic and have been implicated in the rising incidence of many cancers.
If the filtering and/or detoxification systems within the liver are overloaded or inefficient, this will cause toxins, dead cells and micro-organisms to build up in the blood stream. This will then increase the workload of the immune system, which will become overloaded and irritated. The immune system will then produce excessive inflammatory chemicals and in some cases, auto-antibodies because it is in a hyper-stimulated state. This may lead to symptoms of immune dysfunction such as allergies, inflammatory states, swollen glands, recurrent infections, chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia or auto-immune diseases. Some of the more common auto-immune diseases are systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), sclerosing cholangitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, vasculitis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Immune dysfunction is common in the chemically overloaded environment we live in today and is exacerbated by nutritional deficiencies inherent in processed and high fat diets. These symptoms of immune dysfunction often get treated by suppressive drugs.
Rarely does anyone think about the liver, which seems incredible to me because it is such a powerful organ. Indeed it is obvious that the simplest and most effective way to cleanse the blood stream and thus take the load off the immune system is by improving liver function.
Improve Your Liver Function
Liver tonics are helpful for the liver in many ways and can be obtained in powder and capsule form. A good liver tonic needs to contain a synergistic mixture of natural ingredients to support the detoxification pathways in the liver and enhance the structural and functional integrity of the liver cells and sinusoidal liver filter. I recommend an excellent liver tonic called "Livatone Plus" which contains a combination of herbs, anti-oxidants, B vitamins, minerals and amino acids to support the detoxification pathways in the liver. This is available through The Nutri Centre, 7 Park Crescent, London WIN 3HE. For information call 0171-436 5122.
Let us take a look at the various natural ingredients that are found in Livatone Plus.
Cruciferous Vegetables
Broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage and Brussels sprouts contain various compounds such as indoles, thiols and sulphur compounds which enhance the liver's phase two detoxification pathways. There is evidence that cruciferous vegetables are able to reduce the risk of cancer and the American Cancer Society have been placing large advertisements in magazines with pictures of these vegetables saying that "A defence against cancer can be cooked up in your kitchen".
Green Tea
Green tea exerts strong antioxidant actions and is also able to inhibit cancer cell growth. The Chinese, who are large drinkers of green tea, have a 60% less chance of oesophageal cancer. Parts of Japan where people drink a lot of green tea, have a lower incidence of many types of cancers, including stomach, oesophageal and liver cancer.
Green tea may also be of benefit as an aid to weight loss through positive effects on fat and sugar metabolism.
Amino Acids
Specific amino acids are essential for the liver to break down toxins and drugs and also for the efficient metabolism of nutrients by the liver
Glutamine
This amino acid is required for phase two detoxification in the liver and is required in increased amounts by those who consume excessive alcohol. It is able to reduce the craving for alcohol.
Glutamic acid is a constituent of glutathione, which is essential for liver phase two conjugation reactions used during detoxification. The body produces glutathione from the amino acids glycine, glutamic acid and cysteine.
Glutathione is a potent antioxidant that is produced in the healthy liver where it neutralises oxygen molecules before they can damage cells.
Glutathione is a component of the antioxidant enzyme glutathione-S-transferase, which is a widely acting liver-detoxifying enzyme. Indeed large amounts of glutathione are stored in the liver, where it detoxifies harmful compounds so they can then be excreted via the bile.
Glutathione helps to reduce damage from cigarette smoke, alcohol, radiation, heavy metals, drugs and chemotherapy. It plays a role in preventing liver cancer and may also retard ageing.
With ageing glutathione levels decline and if this is not corrected the ageing process is accelerated. It is not worth taking glutathione supplements, as they are expensive and poorly absorbed. It is far more effective to increase glutathione levels by giving the raw materials the liver needs to make its own glutathione, namely the amino acids glycine, glutamic acid and cysteine.
Glycine
This amino acid performs more biochemical functions than any other amino acids, and is required for the synthesis of bile salts and is used by the liver to detoxify chemicals in the phase 2 detoxification pathways.
Taurine
Taurine plays a major role in good liver function via detoxification and the formation of bile. Inadequate levels of taurine are common in many patients with chemical sensitivities and allergies. Taurine is the major amino acid required by the liver for the removal of toxic chemicals and metabolites from the body. Impaired body synthesis of taurine will reduce the ability of the liver to detoxify environmental chemicals such as chlorine, chlorite (bleach), aldehydes (produced from alcohol excess), alcohols, petroleum-based solvents and ammonia. Recent findings are demonstrating, that taurine is one of the major nutrients involved in the body's detoxification of harmful substances and drugs, and should be considered in the treatment of all chemically sensitive patients. Taurine is helpful for high blood cholesterol and gall bladder problems, alcohol withdrawal, hepatitis and jaundice.
Cysteine
Cysteine is an amino acid that contains sulphur and is needed by the phase-two detoxification pathway. It is a precursor of glutathione, which is needed to breakdown pollutants and toxins and has powerful antioxidant effects. Aldehydes, which are toxic breakdown products of alcohol, rancid fats and smog, are partially neutralised by cysteine. A study reported that large doses of acetaldehyde, (derived from alcohol) killed 90% of the rats who consumed it. A control group of rats were primed with vitamin C, B 1 and cysteine and were then given the equivalent amount of acetaldehyde that had killed 90% of the other mice. None of the supplement-primed mice in the control group died.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants destroy free radicals and so help to detoxify and protect the cells of the body, including the liver cells, from toxins.
Vitamin C
Vitamin C or ascorbic acid is the most powerful antioxidant for the liver and reduces toxic damage to the liver cells from chemical overload. It neutralises free radicals generated during the phase 1 detoxification pathway in the liver. Toxic chemicals are far less dangerous if there is plenty of vitamin C in the liver. It helps the liver to regulate cholesterol levels and improves immunity.
Vitamin E
Natural vitamin E is biologically more active than synthetic vitamin E.
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects fats from damage. Since cell membranes are composed of fats, vitamin E is the best protector of cell membranes. It does this by preventing free radicals from oxidising cell membranes, which prevents them from becoming rancid. Thus vitamin E can help to protect the membranes surrounding liver cells. Vitamin E is also needed in those with a "fatty liver", where there is an accumulation of unhealthy oxidised fats in the liver cells.
Natural Carotenoids
Carotenoids such as betacarotene, are most commonly found in fruits and vegetables and are most significant for human health. It is important to take only natural sources of beta-carotene and other carotenoids.
Beta-carotene gets converted in the body to vitamin A and yet has none of the toxic side effects of high doses of vitamin A. Large population studies have shown that low intakes of beta-carotene are associated with a higher incidence of cancer. Beta-carotene is a powerful protective antioxidant.
B Vitamin Group
Thiamine (Vitamin B1)
This B vitamin has antioxidant properties and is helpful in reducing the toxic effects of alcohol, smoking and lead. Thiamine protects against many of the metabolic imbalances caused by alcohol. Deficiency of thiamine is common in those who consume excessive alcohol and this will cause poor mental function.
Riboflavine (Vitamin B2)
This B vitamin is required during phase one detoxification in the liver and is crucial in the production of body energy. Riboflavine deficiency is common in those who consume excessive alcohol and should be supplemented.
Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3)
This is also known as Niacinamide and is required by the liver's phase one detoxification system. It is needed for the metabolism of fats and helps to keep cholesterol levels under control.
Calcium Pantothenate (Vitamin B5)
Several studies have found that pantothenate can lower cholesterol (by an average of 15%) and triglycerides (by an average of 30%) in those with elevated levels of these blood fats. A study showed that pantothenate speeds up liver detoxification of acetaldehyde after alcohol consumption. This is very important for those who consume excessive alcohol because acetaldehyde appears to be a major chemical in the toxic process that accompanies long term alcohol use. Pantothenate is required in increased amounts by those who use alcohol excessively, and in liver disease.
Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6)
Vitamin B6 is required for effective phase-one liver detoxification, and is essential for physical and mental health. Vitamin B6 inhibits the formation of a toxic chemical called homocysteine, which accelerates cardiovascular disease.
Vitamin B12
This powerful vitamin is essential for those who are strict vegetarians or those with nervous complaints. It is a great energiser of the nervous system and can reduce depression and fatigue. It is required for phase one detoxification of chemicals in the liver, and can help people who are allergic to sulphites, which are common food and wine additives. A study showed that vitamin B12 can effectively block most of the adverse reactions to sulphites such as hay fever, sinus, headache and bronchial spasms. B12 is required in increased amounts by those who use alcohol excessively or in liver disease.
Folic Acid
Is required for the phase one detoxification pathway in the liver and for cell repair and division. There is an increased need in alcohol excess.
Some studies have shown that folic acid exerts an anti-cancer effect.
Biotin
Biotin is one of the B vitamins and is produced in the intestines by friendly bacteria and is found in foods such as nuts, whole grain foods, vegetables and brewer's yeast and in supplement form. Liver cells that lack biotin will be deprived of the energy they need to detoxify chemicals and drugs.
Deficiency of this vitamin is not rare and can cause hair loss, dry flaky skin, rashes and fatigue. Those with a poor diet, alcoholism or long term antibiotic use are at risk of deficiency.
Inositol
This vitamin is important in fat metabolism and helps to remove fats from the liver. Deficiency of inositol can increase hardening of the arteries, increased blood cholesterol levels and lead to hair loss, constipation and mood swings. Excessive consumption of caffeine can reduce the level of inositol in the body.
Lecithin
Lecithin contains healthy fats, which are required for the functional and structural integrity of cell membranes. Lecithin is composed of the B vitamin choline along with linoleic acid and inositol. Lecithin is vital for fat metabolism and allows cholesterol to disperse in water so that it can be transported around the body to where it is needed or removed from the body. This reduces the risk of fatty degeneration in arteries and vital organs. It can help those with the condition of fatty liver caused by incorrect diet or alcoholism.
Zinc
The mineral zinc has antioxidant properties and forms part of the powerful antioxidant enzyme called superoxide dismutase (SOD). It is vital for the efficient functioning of the cellular immune system.
St. Mary's Thistle (Milk Thistle)
Milk Thistle, also known as "Silybum Marianum", is a herb with remarkable detoxifying and liver protective effects.
Research has shown that milk thistle can protect against some severe liver toxins. For example the poisonous mushroom Amanita phalloides leads to death in 40% of people who ingest it. This mushroom contains the toxins, phalloidin and amanitin, which are highly destructive to liver cells. Extracts of milk thistle containing the active ingredient silymarin, which is a bioflavonoid can protect the liver from phalloidin. Some animal experiments found that silymarin was 100% effective in preventing toxicity when given before poisoning by the mushrooms. Silymarin was also effective if given to the poisoned animals within 10 minutes after ingestion. Furthermore if silymarin was given within 24 hours after ingestion it still prevented death and greatly reduced the severity of liver damage. Silymarin also protects the liver in animals exposed to alcohol and the solvent carbon tetrachloride.
Liver disorders in humans have been treated with silymarin with promising results. Patients with chronic hepatitis (liver inflammation) had improvements in liver function after taking silymarin for 3 months. Most liver toxins, including alcohol, produce damage to cell membranes via free radical generation. Silymarin functions as an antioxidant and reduces damage to cell membranes.
Principles of the Liver Cleansing Diet
1 Eat plentiful amounts of raw fruits and vegetables, especially dark green leafy vegetables and orange and red coloured fruits and vegetables. Forty percent of the diet should consist of raw fruits and vegetables.
2 Avoid the fats that present a high workload for the liver such as dairy products, processed vegetable oils (hydrogenated fats), deep fried foods, foods that are not fresh and contain rancid fats, preserved meats and fatty meats. In those with a dysfunctional liver, I recommend avoiding all animal milks and substituting them with oat, rice, almond or soy milks.
3 Eat the "good fats" which contain essential fatty acids found in cold pressed vegetable and seed oils, avocados, fish, flaxseed, raw nuts and seeds (must be fresh) and legumes. Seeds such as flaxseeds can be ground freshly everyday (in a regular coffee grinder or food processor) and can be added to cereals, smoothies, fruit salads and vegetables. Replace butter and margarine with tahini, humus, nut spreads, avocado or honey. The good fats are essential to build healthy cell membranes around the liver cells.
4 Avoid artificial chemicals and toxins such as insecticides, pesticides, artificial sweeteners (especially aspartame), colourings, flavourings and preservatives. Excess alcohol, particularly spirits should be avoided. Try not to drink more than 2 glasses of beer or wine daily if you have a liver problem, and do not drink alcohol everyday. Reduce coffee to two cups daily, and ground natural coffee is better than instant coffee powders.
5 Consume a diverse range of proteins from grains, raw nuts, seeds, legumes, eggs, seafood, and if desired, free range chicken and lean fresh red meats. It is safe to be a vegetarian, however, you may need to take supplements of vitamin B12, iron, taurine and carnitine to avoid poor metabolism and fatigue. To obtain first class protein, strict vegetarians need to combine 3 of the following at one meal – grains, nuts, seeds, legumes, otherwise valuable essential amino acids may be deficient.
6 Use natural sugars from fresh fruits and juices, dried fruits, honey, molasses, fruit sorbet ice-creams, fruit cakes, fruit jams, carob, date sugar, maple sugar or syrup or rice syrup.
7 Drink large amounts of fluids such as water, raw juices, teas (green tea, herbal and regular weak tea are fine). Aim for 2 litres of fluid daily and this will avoid constipation problems. Use a household water filter. The best are those with sub-micron-solid carbon-block filters as they are able to remove parasites and many toxic chemicals.
8 Try to find a source of organically grown fruits and vegetables and hormone and antibiotic free meat. It is important to increase consumer demand for these products. Avoid foods that are not fresh.
9 Avoid constipation by having plenty of fibre found in unprocessed food and raw fruits and vegetables and do not overeat. Consistently overeating greatly increases the workload of the liver and this may reduce its capacity to detoxify harmful substances efficiently.
10 Eat foods to increase nutrients beneficial to liver function. These are:
Vitamin K – green leafy vegetables and alfalfa sprouts
Arginine – this helps the liver to detoxify ammonia – found in legumes (beans, peas, lentils) and seeds
Antioxidants – protective and cleansing-found in fresh raw juices such as carrot, celery, beetroot, dandelion, apple, pear and green drinks like wheat-grass juice and spirulina and fresh fruits particularly citrus and kiwi fruit.
Selenium – sources of the antioxidant selenium are brazil nuts, brewers yeast, kelp, brown rice, liver, molasses, seafood, wheatgerm, whole-grains, garlic and onions.
Methionine – essential for detoxification – found in legumes, eggs, fish, garlic, onions, seeds and meat.
Essential fatty acids – flaxseed (ground and fresh), oily fish, avocado, fresh raw nuts and seeds, cold pressed fresh vegetable and seed oils, evening primrose oil, black-currant seed oil, star flower oil.
Natural sulphur – garlic, onions, leeks, shallots, cruciferous vegetables such as broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage and Brussels sprouts.
The Liver Flush
For patients who feel that they need to stimulate the elimination of toxins and waste products from the body, a liver flush can be done to increase the flow of bile and improve liver function. This also helps to purify the blood stream and lymphatic system.
Program for the liver flush
1 Freshly squeeze some citrus juices such as grapefruit, orange, lemon and limes to make 300 mls of juice. This will have a slightly sour taste, which is good as bitter tasting fruits and vegetables have a cleansing effect upon the liver. Dilute the juice with 200 mls of filtered water.
2 Grate 1 to 2 cloves of fresh garlic and a small amount of ginger root and then press this in a garlic press to make juice. Add this juice to the water and citrus juice mixture. Garlic and ginger are liver cleansing and protective and garlic contains sulphur compounds that the liver requires for its detoxification enzymes.
3 Add 1 tablespoon of cold pressed virgin olive oil and mix in a blender with the other juice. Drink this mixture slowly.
4 Follow this with 2 cups of cleansing herbal teas made from 3 to 4 different herbs. Good cleansing herbs to choose from are fennel, dandelion root, burdock root, peppermint, fenugreek, red clover, cleavers, chickweed, nettle and parsley root.
Do this liver flush in the morning after some brisk walking and deep breathing exercises. Then lie down and do not eat for two hours after the flush. Make sure you drink 2 litres of water gradually by sipping slowly during the day after you have done the morning liver flush. This can be done every morning for one week and may be done twice a year.
I recommend that the liver flush and use of herbal teas are supervised by a qualified health practitioner.
Some hints on making herbal teas
An infusion is best for leaves, flowers and other light parts of a plant. This is made by bringing water to a boil, taking it off the heat, adding the herbs, and then covering the pot and leaving the mixture to steep for 15 to 20 minutes. Strain and drink when warm and if desired sweeten with a small amount of honey. For herbal infusions the general ratio of herbs to water is 1:20 (e.g. one ounce of herbs to 20 ounces of water).
A decoction is best for heavier parts of plants such as bark, roots or seeds. To make a decoction simmer the herbs in filtered water for 30 to 60 minutes. Strain and drink when warm and sweeten with a small amount of honey if desired. For decoctions the general ratio of herbs to water is 1:10. These ratios are general guidelines and may be varied considerably by your herbalist.
It is preferable to make herbal teas in glass, ceramic, stainless steel or clay pots and aluminium or Teflon coated saucepans or pans should not be used.
Although the liver is the major organ involved in detoxification, it is still important to support the other body organs of elimination, because this will reduce the work load of the liver. The skin and the kidneys eliminate toxins through sweating and urine and this is why saunas and a high intake of filtered water can reduce symptoms of toxic overload.
It is possible to mitigate against toxic chemical damage by following a diet to support the metabolic and cleansing functions of the liver and by taking specific nutrients that support the detoxification pathways of the liver and reduce the amount of reactive organic chemicals and their intermediaries.
More than ever before in the course of history we need to utilise the power of nutritional medicine to chart a safe passage through the chemical waters and atmosphere that will take us time to repair. Let us hope that time is a luxury we still have.
References
Saint Mary's Thistle
Floersheim GL et al. Effects of penicillin and silymarin on liver enzymes and blood clotting factors in dogs given a boiled preparation of Amanita phalloides. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology. 46:455-462, 1978
Valenzuela A. et al. Silybin dihemisuccinate protects rat erythrocytes against phenylhydrazine-induced lipid peroxidation and haemolysis. Planta Medica. 53:402-405,1987.
Valenzuela A. et al. Silymarin protection against hepatic lipid peroxidation induced by acute ethanol intoxication in the rat. Biochemical Pharmacology.34:2209-2212,1985.
Vengerovski AI et al. Liver protective action of silybinene in experimental CCL4 poisoning. Farmakologiya I Toksikologiya. 50:67-69,1987
Wagner H. Antihepatoxic flavonoids. Progress in Clinical and Biology Research. 213:319-331,1986
Selenium
Boost Your Energy. Dr. Sandra Cabot, 1997, Women's Health Advisory Service
Margaret Rayman, "Dietary Selenium: time to act", British Medical Journal, Vol. 314, 387, Feb 1997
Taurine
Orthoplex Research Bulletin, "Taurine the detoxifying amino acid". Nutrients in profile, Henry Osieki. Bioconcepts Publishing.
Olive Leaf Extract – Nature's Antibiotic, Dr. Morton Walker, Kensington Publishing Corp.
Pantothenate
Arsenio L et al. Effectiveness of long term treatment with pantothenate in patients with dyslipidaemia. Clinical Therapeutics. 8:537-541, 1986
Gaddi A et al. Controlled evaluation of pantothenate: A natural hypolipidaemic compound in patients with different forms of hyperlipoproteinaemia. Atherosclerosis. 50:73-83, 1984.
Watanabe A et al. Lowering of blood acetaldehyde but not ethanol concentration by pantothenate following alcohol ingestion. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 9 (3):272-276,1985
Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 confirmed as effective sulphite allergy blocker. Allergy Observer. 4(2):1, March – April 1987
Beck WS. Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) and the nervous system. N. Eng. J. Med. 318:1752-1754, 1988.
Jacobsen DW. et al. Cobalamin protection in sulphite sensitive asthmatics (SSA), Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (Supplement). 73:135, 1984.
Folic Acid
Froster-Iskenius U et al. Folic acid treatment in males and females with fragile X syndrome. American Journal of Medical Genetics. 23:272-289, 1986
Glutathione
Meister A. Selective modification of glutathione metabolism. Science 220:472-477,1983
The Doctor's Vitamin Encyclopedia, Arrow Books, Dr. Sheldon Hendler. M.D., PhD.
Liver Function
Bland J.S., Bralley J.A., Nutritional up-regulation of hepatic detoxification enzymes. The Journal of Applied Nutrition, 44: No. 3 & 4, 1992
The Physicians Handbook of Clinical Nutrition, Henry Osiecki, Bioconcepts Publishing
The Liver Cleansing Diet Book, Dr Sandra Cabot, W.H.A.S.
Comments:
-
mary said..
Is it best to take Liva Tone Plus ( Powder) first thing in the morning or last thing at night.
Thanks Mary
-
ali said..
How to lose weight even faster Drink More Water and use best rated pills Phen375 find more http://www.fitnessguidefg.com/phen375-review.html
-
Anna said..
Hey,
Thanks for giving this information to us.